An inverter board, often referred to as an inverter circuit or inverter module, is an essential component found in various electronic devices and appliances. Its primary function is to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion is crucial because many electronic devices and appliances, such as laptops, LCD monitors, and air conditioners, require AC power to operate, while they are often powered by DC sources like batteries or power adapters.
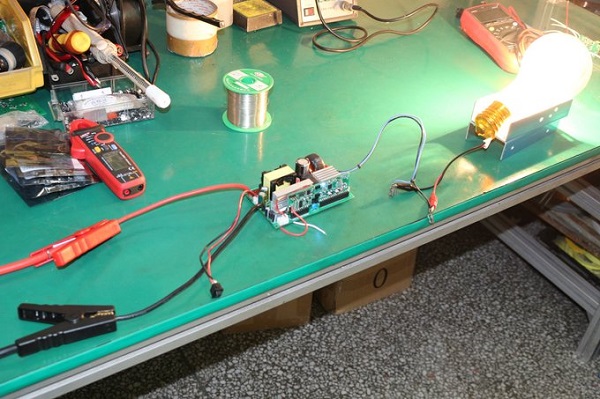
Here’s a more detailed explanation of what an inverter board does:
DC to AC Conversion: The inverter circuit board takes the incoming DC power and generates AC power with a specific voltage, frequency, and waveform, typically a modified sine wave or a pure sine wave, depending on the application. The type of waveform produced can affect the performance of connected devices.
Voltage Regulation: In addition to converting DC to AC, inverter PCB board often include voltage regulation circuitry. This ensures that the AC output voltage remains stable and within the required range, preventing potential damage to connected devices.
Frequency Control: Some power inverter board allow for adjustable output frequencies, which can be useful in applications where precise control over the AC frequency is necessary, such as in motor drives or some specialized equipment.
Protection Features: Many inverter boards come equipped with various protection features, including overload protection, over-voltage protection, and short-circuit protection. These safety mechanisms safeguard both the inverter board and the connected devices from potential damage due to electrical faults.
Cooling Systems: Inverters can generate heat during operation, so they often incorporate cooling systems, such as fans or heat sinks, to dissipate excess heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures.
In summary, an inverter board is a critical component in electronics that enables devices to operate using AC power, even when their power source is DC. These boards are essential in a wide range of applications, from small consumer electronics to larger industrial equipment, and they play a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning and protection of electronic devices.


